Add categorical colors to an existing color set
Usage
add_colors(
given_colors = NULL,
n = 1,
return_type = c("new", "full", "list"),
color_fn = rainbowJam,
check_internal = TRUE,
max_iterations = 50,
min_distance = 30,
step_distance = -1,
use_white = "F5",
method = "cie2000",
do_plot = FALSE,
verbose = FALSE,
seed = 123,
...
)Arguments
- given_colors
charactervector of colors, default NULL.When
given_colorsis NULL,nnew colors will be returned.
- n
integernumber of colors to add togiven_colors- return_type
character, default "new", what colors to return:"new"- return only the newly assigned colors"full"- return input colors and assigned colors together, in order: given, then new colors.
- color_fn
function, defaultrainbowJam().The first argument
nis expected to be the integer number of colors to return, and the function should returnncolor values. Other arguments in...are passed to this function for custom options.Alternatively,
characterinput is expanded usingjamba::color2gradient(), although this process is not well-tested.
- check_internal
logicaldefault FALSE whether to check thecolor_fnoutput for internal color distances. This step improves color output, however is currently time-consuming.For best results,
color_fnshould already provide colors are as distinct from one another as possible, generally true for examplerainbowJam().However when using a function that provides relatively uniform colors, such as
colorspace::rainbow_hcl(), the colors which are most distinct fromgiven_colorsare often also very similar to each other. Thecheck_internal=TRUEalso requires colors fromcolor_fnto meet themin_distancethreshold, which requires a recursive, nested algorithm infind_color_spread().
- max_iterations
integerdefault 50, maximum iterations to attempt. The algorithm begins atnand increases the attempted colors by 1 each iteration until it defines at leastnnew colors.When
step_distanceis non-zero, themin_distanceis reduced byabs(step_distance)then the iterations are repeated.When
step_distanceis zero, if no solution is found it returns 'NULL'.
- min_distance
numericdefault 30, minimum distance to require for new colors compared togiven_colors.When at least
ncolors are defined with at leastmin_distancedistance fromgiven_colors, thencolors with the greatest distance are returned.When
ncolors do not meet these critera, andstep_distanceis non-zero, themin_distanceis reduced byabs(step_distance)and the process is repeated.Finally, if
ncolors cannot be defined, it returns 'NULL'.
- step_distance
numericdefault 1, the default step size when iterating progressively smallermin_distancevalues.When 'NULL' or '0', the
min_distanceis not decreased aftermax_iterationsiterations.
- use_white
characterdefault "F5" representing the white reference, any value recognized byfarver::as_white_ref().The default 'F5' represents 'daylight fluorescent' and in qualitative testing was most effective when defining color distances.
The typical default 'D65' is 'daylight 6500K' and is typically used for neutral daylight without blue (cool) or yellow (warm) shifted background lighting.
- method
character, default 'cie2000', passed toslot_colors(), thencolor_distance()to define the color distance method.- do_plot
logicaldefault FALSE, whether to plot the given_colors and new colors.- verbose
logicalindicating whether to print verbose output.- ...
additional arguments are passed to internal functions
color_fn,slot_colors(), and optionallyjamba::color2gradient().
Details
This function is actively evolving. The core goal is to take
a set of categorical colors, and to add 'n' more colors using
a color function such as rainbowJam(). It will add colors
with maximum color distance, to provide as distinct a set of
colors as possible, based upon the existing colors in use.
The existing colors can be provided from any source, it
does not need to be generated by rainbowJam().
See also
Other colorjam assignment:
col_div_xf(),
col_linear_xf(),
color_complement(),
group2colors(),
matrix2heatColors(),
rainbowJamMulti(),
vals2colorLevels(),
vibrant_color_by_hue()
Examples
n1 <- 6;
n <- 2;
given <- jamba::nameVector(rainbowJam(n1));
new_colors <- add_colors(given, n=n, method="cmc")
names(new_colors) <- seq_along(new_colors);
cdl <- show_color_distance(c(given, new_colors))
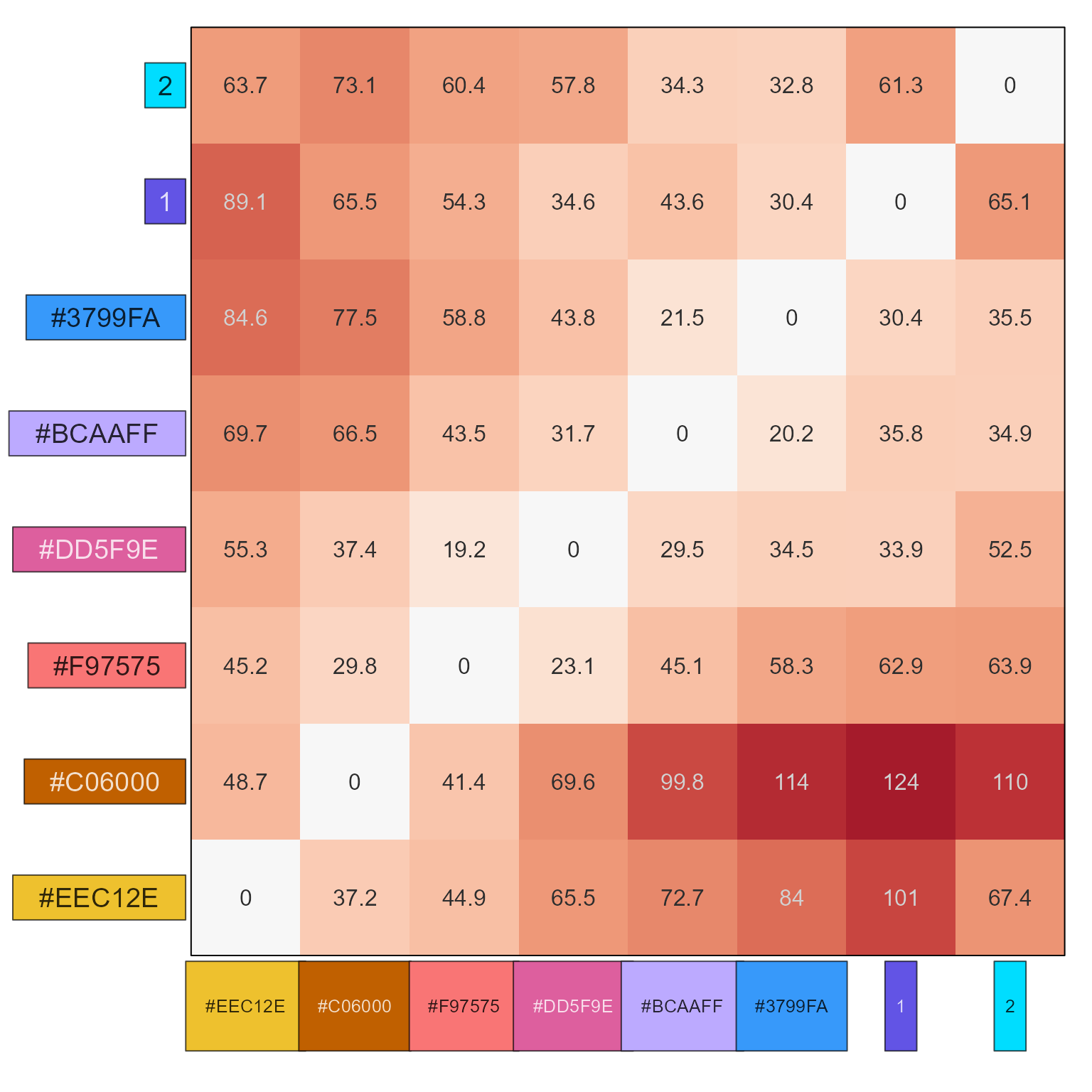 show_color_distance(c(given, new_colors), cluster_data=TRUE)
show_color_distance(c(given, new_colors), cluster_data=TRUE)
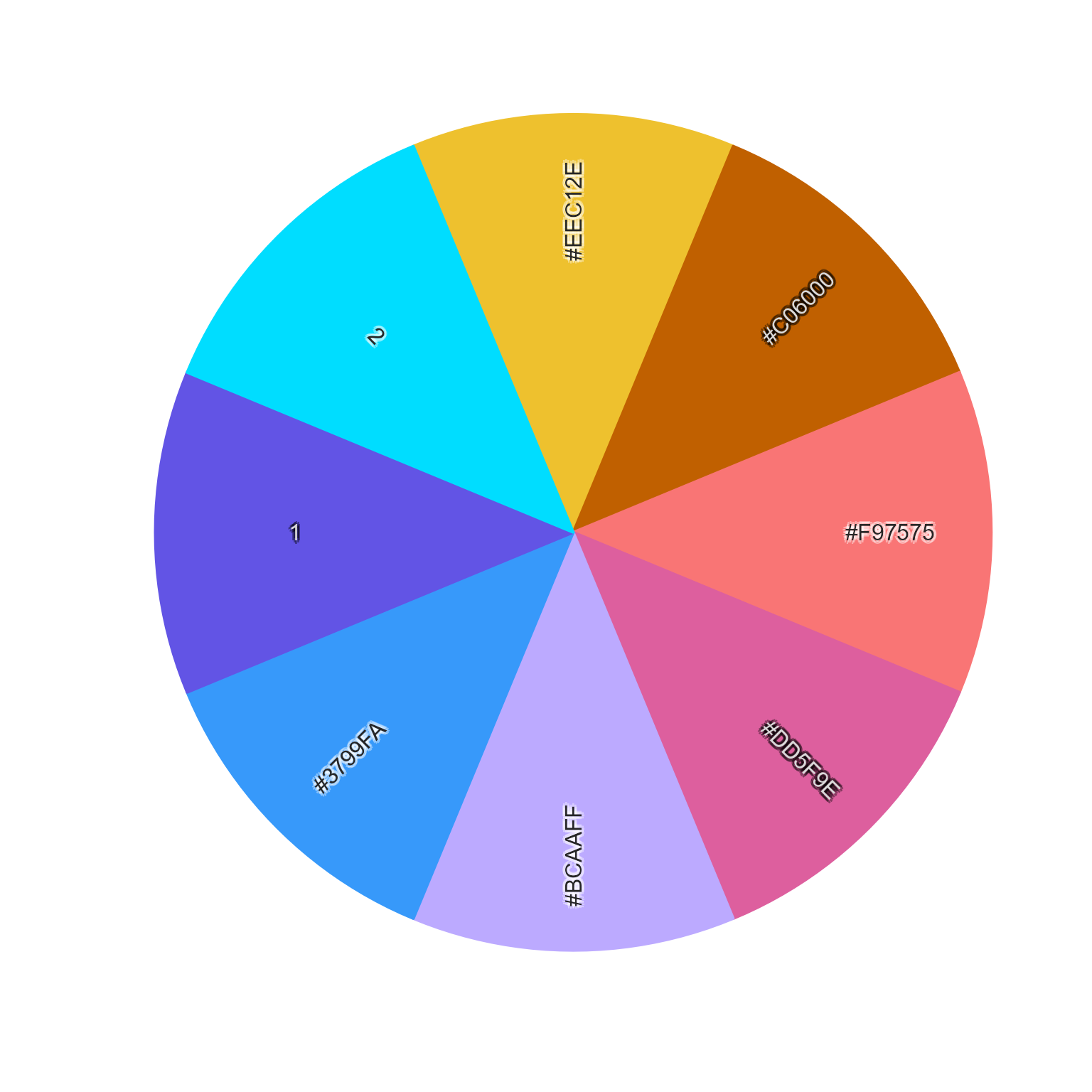
 given2 <- c(given, new_colors);
color_pie(given2)
given2 <- c(given, new_colors);
color_pie(given2)
 new_colors2 <- add_colors(unname(given2), n=n, dist_threshold=15)
color_pie(sort_colors(c(given2, new_colors2)))
new_colors2 <- add_colors(unname(given2), n=n, dist_threshold=15)
color_pie(sort_colors(c(given2, new_colors2)))
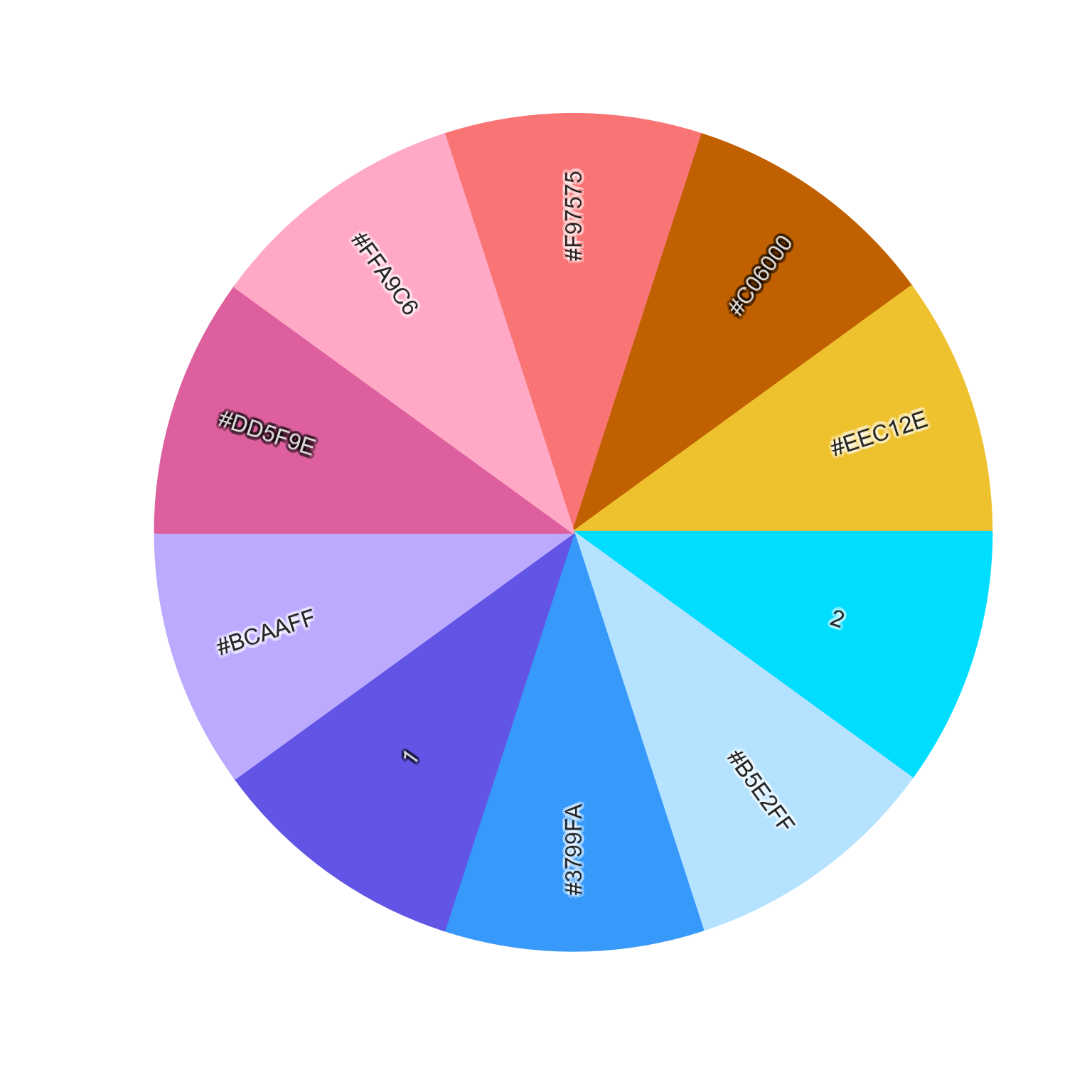 new_colors2 <- add_colors(unname(given2), n=n, dist_threshold=20)
color_pie(sort_colors(c(given2, new_colors2)))
new_colors2 <- add_colors(unname(given2), n=n, dist_threshold=20)
color_pie(sort_colors(c(given2, new_colors2)))
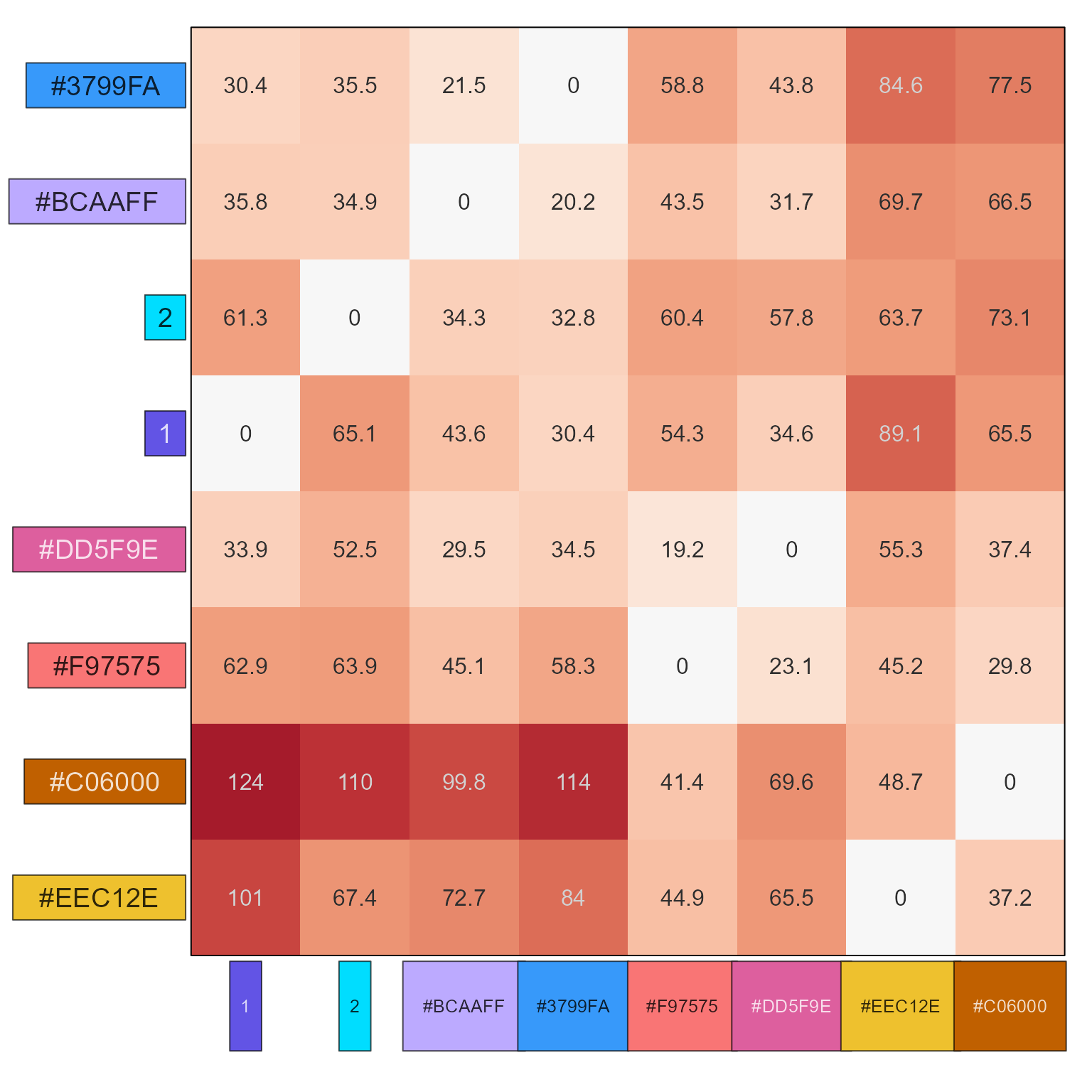
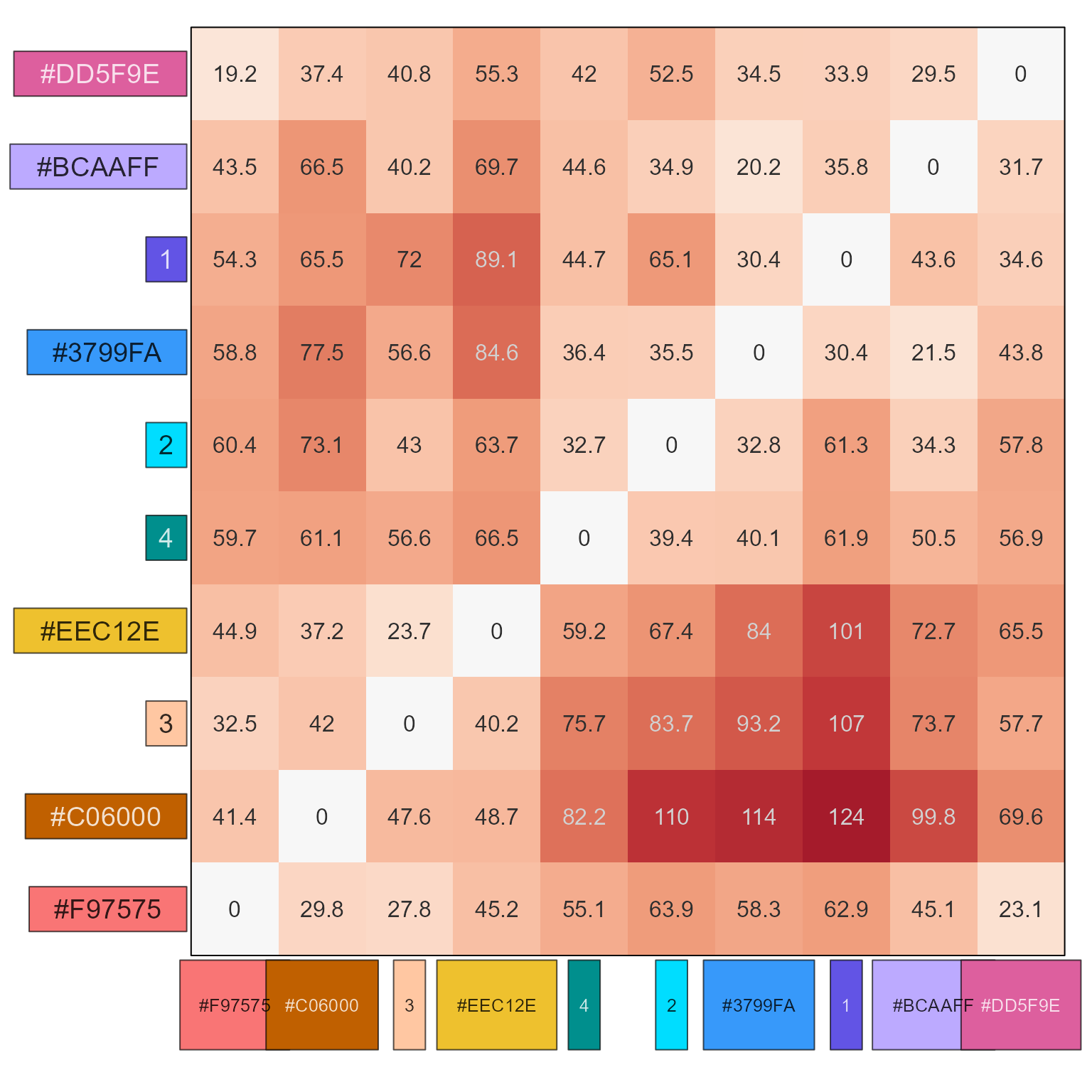
 names(new_colors2) <- seq_along(new_colors2) + 2;
show_color_distance(sort_colors(c(given2, new_colors2)))
names(new_colors2) <- seq_along(new_colors2) + 2;
show_color_distance(sort_colors(c(given2, new_colors2)))
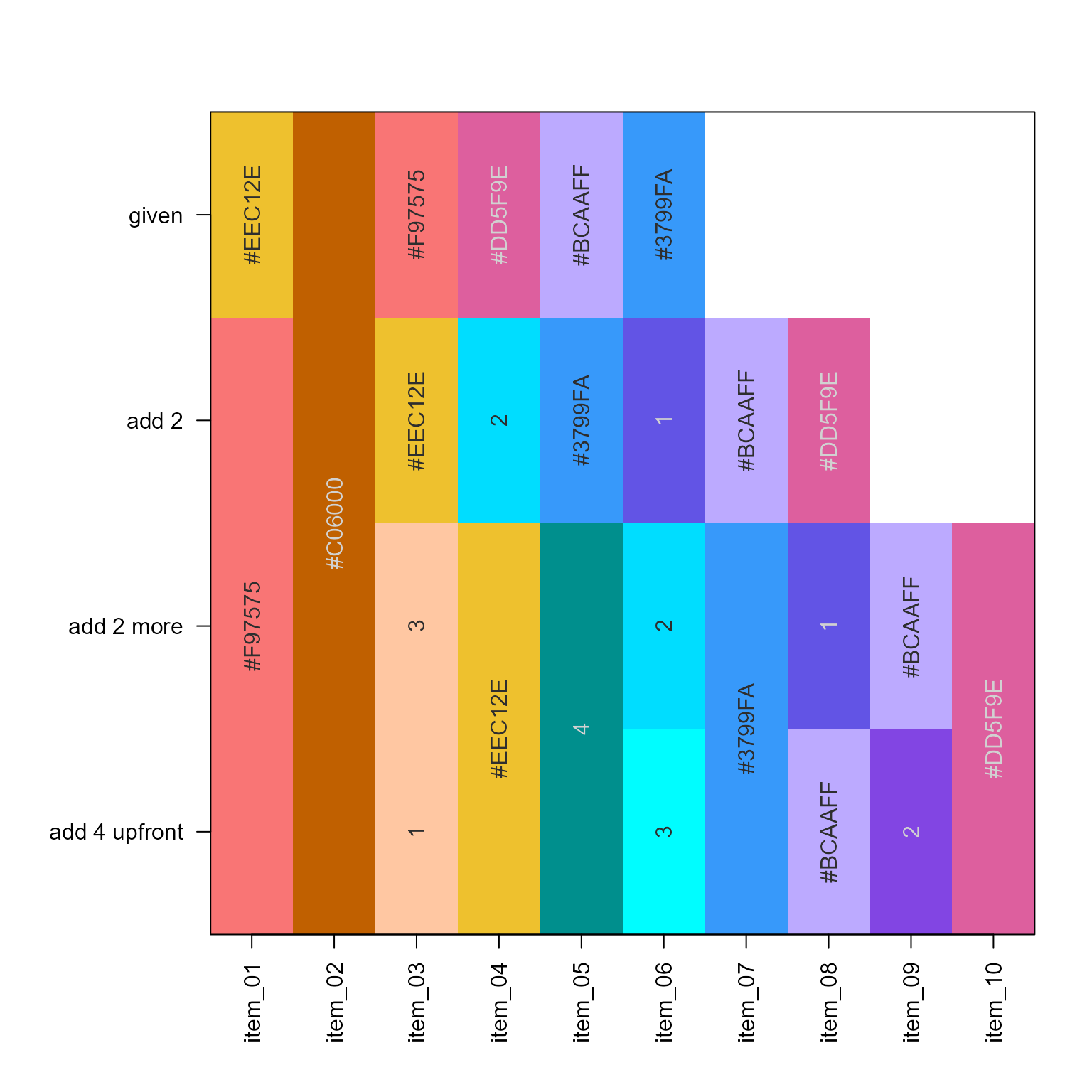
 new_colors4 <- add_colors(given, n=4, dist_threshold=20)
names(new_colors4) <- seq_along(new_colors4);
jamba::showColors(list(given=given,
`add 2`=sort_colors(c(given, new_colors)),
`add 2 more`=sort_colors(c(given2, new_colors2)),
`add 4 upfront`=sort_colors(c(given, new_colors4))))
new_colors4 <- add_colors(given, n=4, dist_threshold=20)
names(new_colors4) <- seq_along(new_colors4);
jamba::showColors(list(given=given,
`add 2`=sort_colors(c(given, new_colors)),
`add 2 more`=sort_colors(c(given2, new_colors2)),
`add 4 upfront`=sort_colors(c(given, new_colors4))))
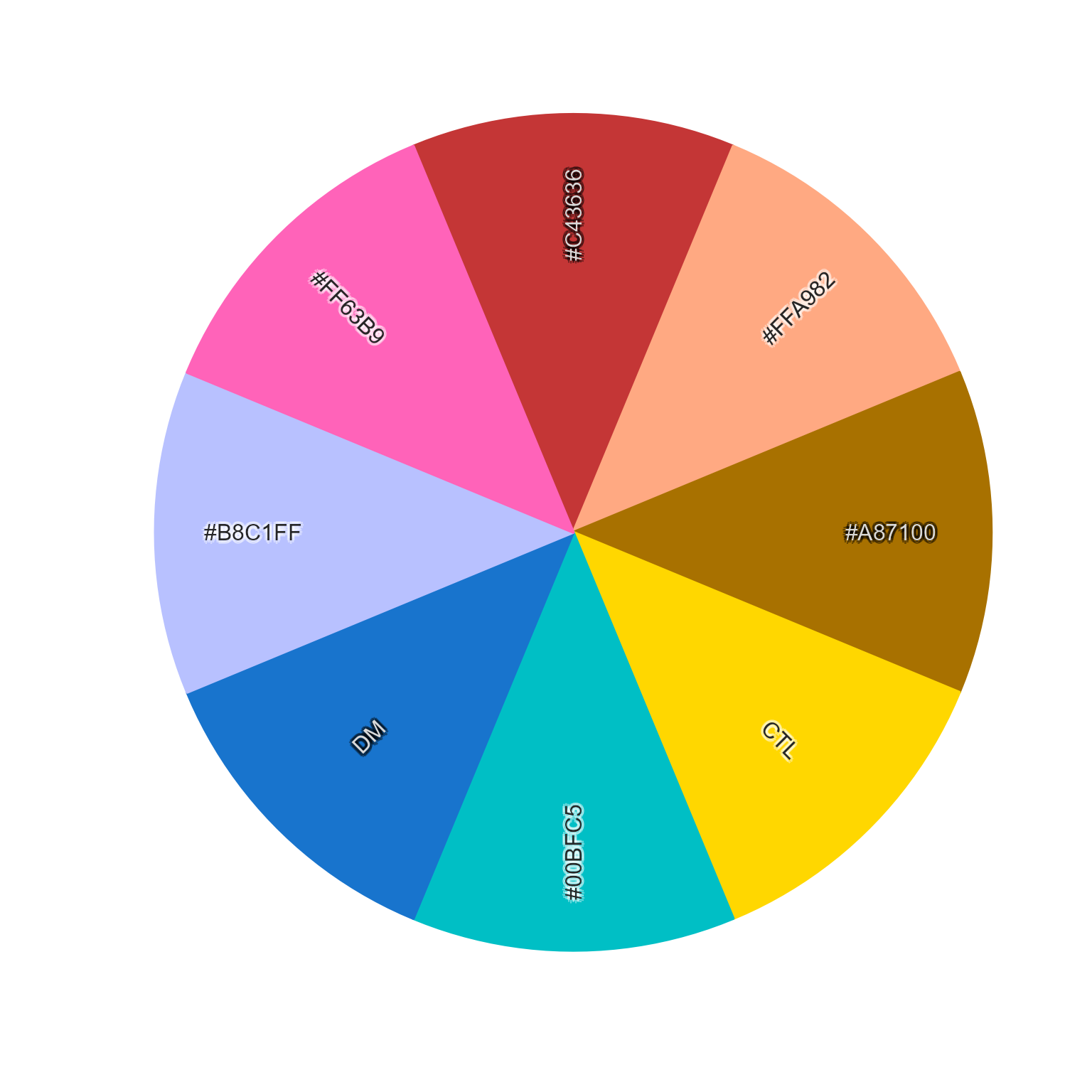
 # test common themes
given <- c(DM="dodgerblue3", CTL="gold")
new6 <- add_colors(unname(given), n=6)
color_pie(sort_colors(c(given, new6)))
# test common themes
given <- c(DM="dodgerblue3", CTL="gold")
new6 <- add_colors(unname(given), n=6)
color_pie(sort_colors(c(given, new6)))