Export a data.frame to 'Excel' 'xlsx' format
Usage
writeOpenxlsx(
x,
file = NULL,
wb = NULL,
sheetName = "Sheet1",
startRow = 1,
startCol = 1,
append = FALSE,
headerColors = c("lightskyblue1", "lightskyblue2"),
columnColors = c("aliceblue", "azure2"),
highlightHeaderColors = c("tan1", "tan2"),
highlightColors = c("moccasin", "navajowhite"),
borderColor = "gray75",
borderPosition = "BottomRight",
highlightColumns = NULL,
numColumns = NULL,
fcColumns = NULL,
lfcColumns = NULL,
hitColumns = NULL,
intColumns = NULL,
pvalueColumns = NULL,
numFormat = "#,##0.00",
fcFormat = "#,##0.0",
lfcFormat = "#,##0.0",
hitFormat = "#,##0.0",
intFormat = "#,##0",
pvalueFormat = "[>0.01]0.00#;0.00E+00",
numRule = c(1, 10, 20),
fcRule = c(-6, 0, 6),
lfcRule = c(-3, 0, 3),
hitRule = c(-1.5, 0, 1.5),
intRule = c(0, 100, 10000),
pvalueRule = c(0, 0.01, 0.05),
numStyle = c("#F2F0F7", "#B4B1D4", "#938EC2"),
fcStyle = c("#4F81BD", "#EEECE1", "#C0504D"),
lfcStyle = c("#4F81BD", "#EEECE1", "#C0504D"),
hitStyle = c("#4F81BD", "#EEECE1", "#C0504D"),
intStyle = c("#EEECE1", "#FDA560", "#F77F30"),
pvalueStyle = c("#F77F30", "#FDC99B", "#EEECE1"),
doConditional = TRUE,
doCategorical = TRUE,
colorSub = NULL,
freezePaneColumn = 0,
freezePaneRow = 2,
doFilter = TRUE,
fontName = "Arial",
fontSize = 12,
minWidth = getOption("openxlsx.minWidth", 8),
maxWidth = getOption("openxlsx.maxWidth", 40),
autoWidth = TRUE,
colWidths = NULL,
wrapCells = FALSE,
wrapHeaders = TRUE,
headerRowMultiplier = 5,
keepRownames = FALSE,
verbose = FALSE,
...
)Arguments
- x
data.frameto be saved to an 'Excel' 'xlsx' file.- file
charactervalid path to save an 'Excel' 'xlsx' file. If the file exists, andappend=TRUEthe new data will be added to the existing file withthe definedsheetName.Note when
file=NULLthe output is not saved to a file, instead theWorkbookobject is returned by this function. TheWorkbookobject can be passed as argumentwbin order to add multiple sheets to the same Workbook prior to saving them together. This operation is intended to provide a substantial improvement in speed.
- wb
Workbookobject as defined in R packageopenxlsx. When this argument is defined, data is not imported fromfile, and instead the workbook data is used fromwb. This option is intended to improve speed of writing several sheets to the same output file, by preventing the slow read/write steps each time a new sheet is added.- sheetName
charactervalue less with a valid 'Excel' 'xlsx' worksheet name. At this time (version 0.0.29.900) the sheetName is restricted to 31 characters, with no puntuation except "-" and "_".- startRow, startCol
integerindicating the row and column number to start with the top,left cell written to the worksheet, default are 1.- append
logicaldefault FALSE, whether to append to file (TRUE), or to write over an existing file. Theappend=TRUEis useful when adding a worksheet to an existing file.- headerColors, columnColors, highlightHeaderColors, highlightColors, borderColor, borderPosition
default values for the 'Excel' worksheet background and border colors. As of version 0.0.29.900, colors must use valid 'Excel' color names.
- highlightColumns, numColumns, fcColumns, lfcColumns, hitColumns, intColumns, pvalueColumns
integervector referring the column number in the inputdata.framexto define as each column type, as relevant.- numFormat, fcFormat, lfcFormat, hitFormat, intFormat, pvalueFormat
characterstring with valid 'Excel' cell formatting, for example"#,##0.00"defines a column to use comma-delimited numbers above one thousand, and display two decimal places in all numeric cells. See[https://support.microsoft.com]topic"Excel Create and apply a custom number format."or"Excel Number format codes"for more details. Some examples below:"#,##0": display only integer values, using comma as delimiter for every thousands place. The number2142.12would be represented:"2,142""###0.0": display numeric values rounded to the0.1place, using no comma delimiter for values above one thousand. The number2142.12would be represented:"2142.1""[>0.01]0.00#;0.00E+00": this rule is a conditional format, values above0.01are represented as numbers rounded to the thousandths position0.001; values below0.01are represented with scientific notation with three digits. The number0.1256would be represented:"0.126"The number0.001256would be represented:"1.26E-03""[Red]#,###.00_);[Blue](#,###.00);[Black]0.00_)": this format applies to positive values, negative values, and zero, in order delimited by semicolons. Positive values are colored red. The string"_)"adds whitespace (defined by"_") equale to the width of the character")"to the end of positive values. Negative values are surrounded by parentheses"()"and are colored blue. Values equal to zero are represented with two trailing digits, and whitespace ("_") equal to width")". The whitespace at the end of positive values and zero are used to align all values at the same decimal position.
- numRule, fcRule, lfcRule, hitRule, intRule, pvalueRule
numericvectorlength=3indicating the breakpoints for 'Excel' to apply conditional color formatting, using the corresponding style. Note that all conditional formatting applied by this function uses the"3-Color Scale", therefore there should be three values, and three corresponding colors in the corresponding Style arguments.- numStyle, fcStyle, lfcStyle, intStyle, hitStyle, pvalueStyle
charactervectorlength=3containing three valid R colors. Note that alpha transparency will be removed prior to use in 'Excel', as required. Note that all conditional formatting applied by this function uses the"3-Color Scale", therefore there should be three colors, which match three values in the corresponding Rule arguments.- doConditional
logicalindicating whether to apply conditional formatting of cells, with this function only the background cell color (and contrasting text color) is affected.- doCategorical
logicalindicating whether to apply categorical color formatting, of only the background cell colors and contrasting text color. This argument requirescolorSubbe defined.- colorSub
charactervector of R colors, whose names refer to cell values in the inputxdata.frame.- freezePaneColumn, freezePaneRow
integervalue of the row or column before which the 'Excel' "freeze panes" is applied. Note that these values are adjusted relative bystartRowandstartColin the 'Excel' worksheet, so that the values are applied relative to thedata.frameargumentx.- doFilter
logicalindicating whether to enable column filtering by default.- fontName
characterdefault font configuration, containing a valid 'Excel' font name.- fontSize
numericdefault font size in 'Excel' point units.- minWidth, maxWidth, autoWidth
numericminimum, maximum size for each 'Excel' cell, in character units as defined by 'Excel', used whenautoWidth=TRUEto restrict cell widths to this range. Note that the argumentcolWidthsis generally preferred, if the numeric widths can be reasonable calculated or anticipated upfront. WhenautoWidth=FALSE'Excel' typically auto-sizes cells to the width of the largest value in each column, which may not be ideal when values are extremely large.- colWidths
numericwidth of each column inx, recycled to the total number of columns required. Note that whenkeepRownames=TRUE, the first column will containrownames(x), therefore the length ofcolWidthsin that case will bencol(x) + 1.- wrapCells
logicaldefault FALSE, indicating whether to enable word-wrap within cells.- wrapHeaders
logicalindicating whether to enable word wrap for column headers, which is helpful whenautoWidth=TRUEsince it fixed the cell width while allowing the column header to be seen.- headerRowMultiplier
numericvalue to define the row height of the first header row in 'Excel'. This value is defined as a multiple of subsequent rows, and should usually represent the maximum number of lines after word-wrapping, as relevant. This argument is helpful whenwrapHeaders=TRUEandautoWidth=TRUE.- keepRownames
logicalindicating whether to includerownames(x)in its own column in 'Excel'.- verbose
logicalindicating whether to print verbose output.- ...
additional arguments are passed to
applyXlsxConditionalFormat()andapplyXlsxCategoricalFormat()as relevant.
Value
Workbook object as defined by the openxlsx package
is returned invisibly with invisible(). This Workbook
can be used in argument wb to provide a speed boost when
saving multiple sheets to the same file.
Details
This function is a minor but useful customization of the
openxlsx::saveWorkbook() and associated functions, intended
to provide some pre-configured formatting of known column
types, typically relevant to statistical values, and
in some cases, gene or transcript expression values.
There are numerous configurable options when saving an 'Excel' worksheet, most of the defaults in this function are intended not to require changes, but are listed as formal function arguments to make each option visibly obvious.
If colorSub is supplied as a named vector of colors, then
by default text values will be colorized accordingly, which
can be especially helpful when including data with categorical
text values.
This function pre-configures formatting options for the following column data types, each of which has conditional color-formatting, defined numeric ranges, and color scales.
- int
integer values, where numeric values are formatted without visible decimal places, and the
big.mark=","standard is used to help visually distinguish large integers. The color scale is by default c(0, 100, 10000).- num
numeric values, with fixed number of visible decimal places, which helps visibly align values along each row.
- hit
numeric type, a subset of "int" intended when data is flagged with something like a "+1" or "-1" to indicate a statistical increase or decrease.
- pvalue
P-value, where numeric values range from 1 down near zero, and values are formatted consistently with scientific notation.
- fc
numeric fold change, whose values are expected to range from 1 and higher, and -1 and lower. Decimal places are by default configured to show one decimal place, to simplify the 'Excel' visual summary.
- lfc
numeric log fold change, whose values are expected to be centered at zero. Decimal places are by default configured to show one decimal place, to simplify the 'Excel' visual summary.
- highlight
character and undefined columns to be highlighted with a brighter background color, and bold text.
For each column data type, a color scale and default numeric range is defined, which allows conditional formatting of cells based upon expected ranges of values.
A screenshot of the file produced by the example is shown below.
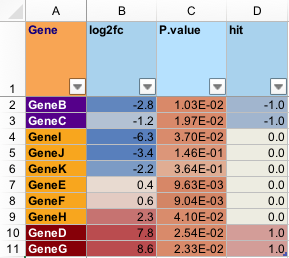
See also
Other jam export functions:
applyXlsxCategoricalFormat(),
applyXlsxConditionalFormat(),
readOpenxlsx(),
set_xlsx_colwidths(),
set_xlsx_rowheights()
Examples
# set up a test data.frame
set.seed(123);
lfc <- -3:3 + stats::rnorm(7)/3;
colorSub <- nameVector(
rainbow2(7),
LETTERS[1:7])
df <- data.frame(name=LETTERS[1:7],
int=round(4^(1:7)),
num=(1:7)*4-2 + stats::rnorm(7),
fold=2^abs(lfc)*sign(lfc),
lfc=lfc,
pvalue=10^(-1:-7 + stats::rnorm(7)),
hit=sample(c(-1,0,0,1,1), replace=TRUE, size=7));
df;
#> name int num fold lfc pvalue hit
#> 1 A 4 0.7349388 -9.106049 -3.1868252 2.780730e-02 0
#> 2 B 16 5.3131471 -4.218488 -2.0767258 6.122279e-01 1
#> 3 C 64 9.5543380 -1.395160 -0.4804306 3.146665e-03 -1
#> 4 D 256 15.2240818 1.016424 0.0235028 1.079898e-06 -1
#> 5 E 1024 18.3598138 2.060645 1.0430959 5.027544e-05 0
#> 6 F 4096 22.4007715 5.945047 2.5716883 3.366732e-07 0
#> 7 G 16384 26.1106827 8.898972 3.1536387 8.554139e-09 1
# write to tempfile for examples
if (check_pkg_installed("openxlsx")) {
out_xlsx <- tempfile(pattern="writeOpenxlsx_", fileext=".xlsx")
writeOpenxlsx(x=df,
file=out_xlsx,
sheetName="jamba_test",
colorSub=colorSub,
intColumns=2,
numColumns=3,
fcColumns=4,
lfcColumns=5,
pvalueColumns=6,
hitColumn=7,
freezePaneRow=2,
freezePaneColumn=2,
append=FALSE);
# now read it back
df_list <- readOpenxlsx(xlsx=out_xlsx);
sdim(df_list)
}
#> rows cols class
#> jamba_test 7 7 data.frame