Mean arc angle in degrees
Arguments
- x
numericvector of angles in degrees.- use_range
logicalindicating whether to return the mean degree angle across the range, which therefore only uses the first and last angular values.- use_median
logicalindicating whether to usemedian()instead ofmean(), included here for convenience.- do_plot
logicalwhether to plot the result, default FALSE.- ...
additional arguments are ignored.
Details
This function differs from mean_degrees() in that it finds
the mean angle in degrees from angles along an arc, guaranteeing
that the mean angle is along that numeric arc. It is intended
that the arc does not cover more than 360 degrees, and for angles
whose numeric values are increasing.
The specific purpose is to enable supplying two angles like c(12, 45) to imply the arc "from 12 to 45 degrees", for which the mean is 28.5. Or one could supply c(45, 12) and imply "from 45, around 360, back to 12 degrees" and the mean of this large arc would be 208.5.
See also
Other venndir geometry:
degrees_to_adj(),
diff_degrees(),
display_angles(),
mean_degrees(),
rescale_coordinates(),
spread_degrees(),
three_point_angle()
Examples
set.seed(1);
steps <- sample((1:12)^1.5, size=14, replace=TRUE);
steps <- sort(steps);
x <- cumsum(steps);
x;
#> [1] 1.000000 2.000000 4.828427 7.656854 12.853007 20.853007
#> [7] 32.033347 43.213686 61.733946 80.254205 107.254205 138.876981
#> [13] 175.359854 211.842727
withr::with_par(list("mfrow"=c(2, 3)), {
mean_degree_arc(x, do_plot=TRUE);
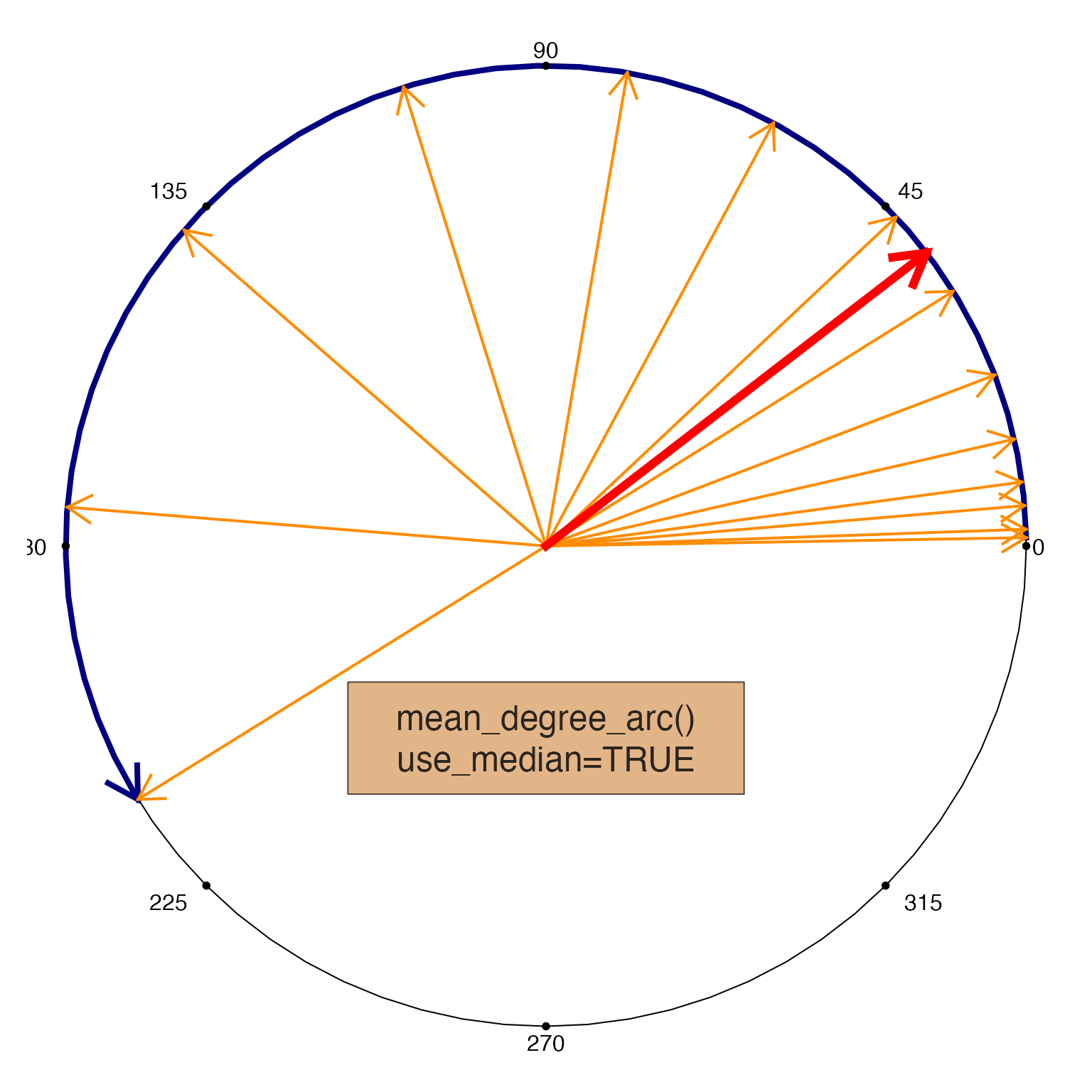
mean_degree_arc(x, use_median=TRUE, do_plot=TRUE);
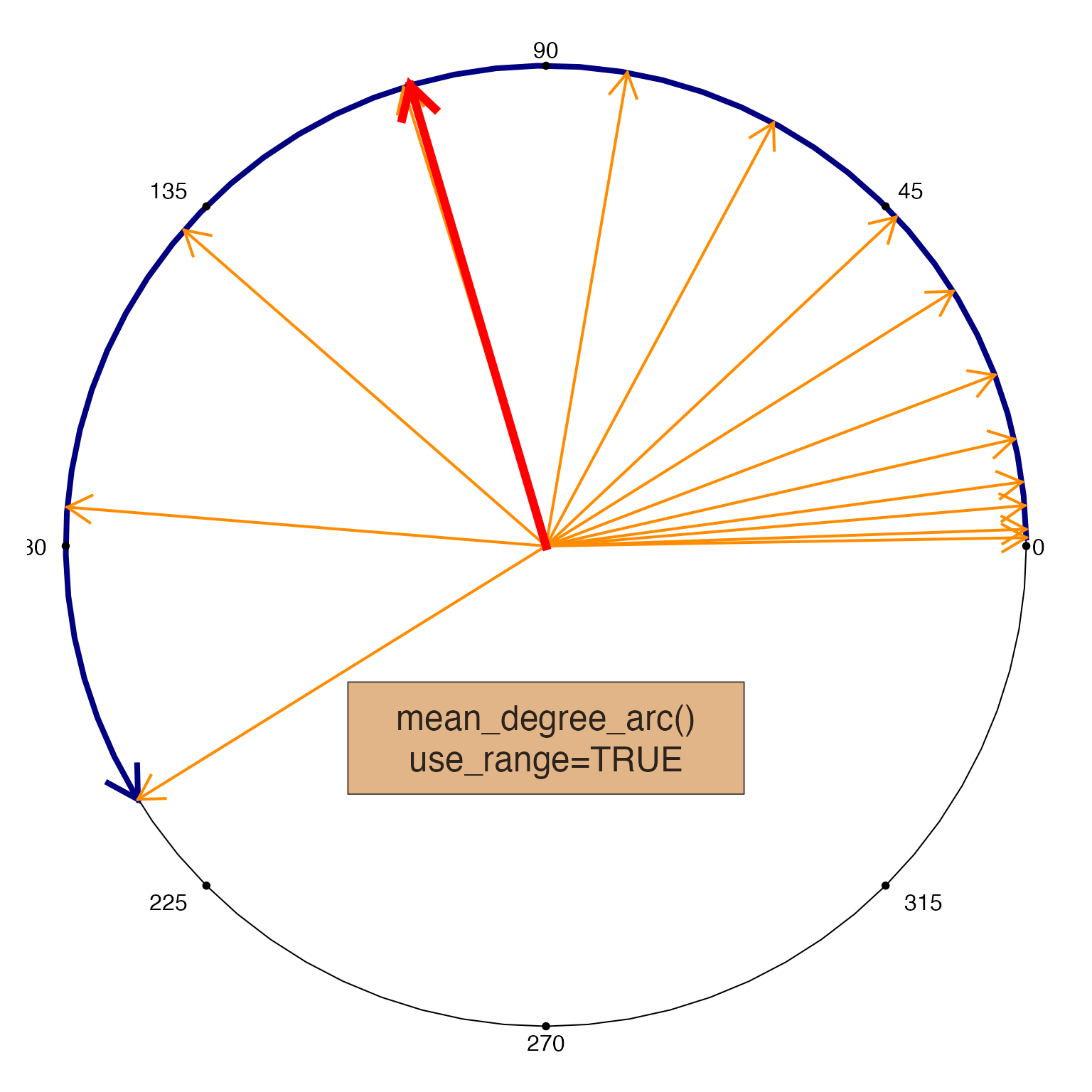
mean_degree_arc(x, use_range=TRUE, do_plot=TRUE);
})
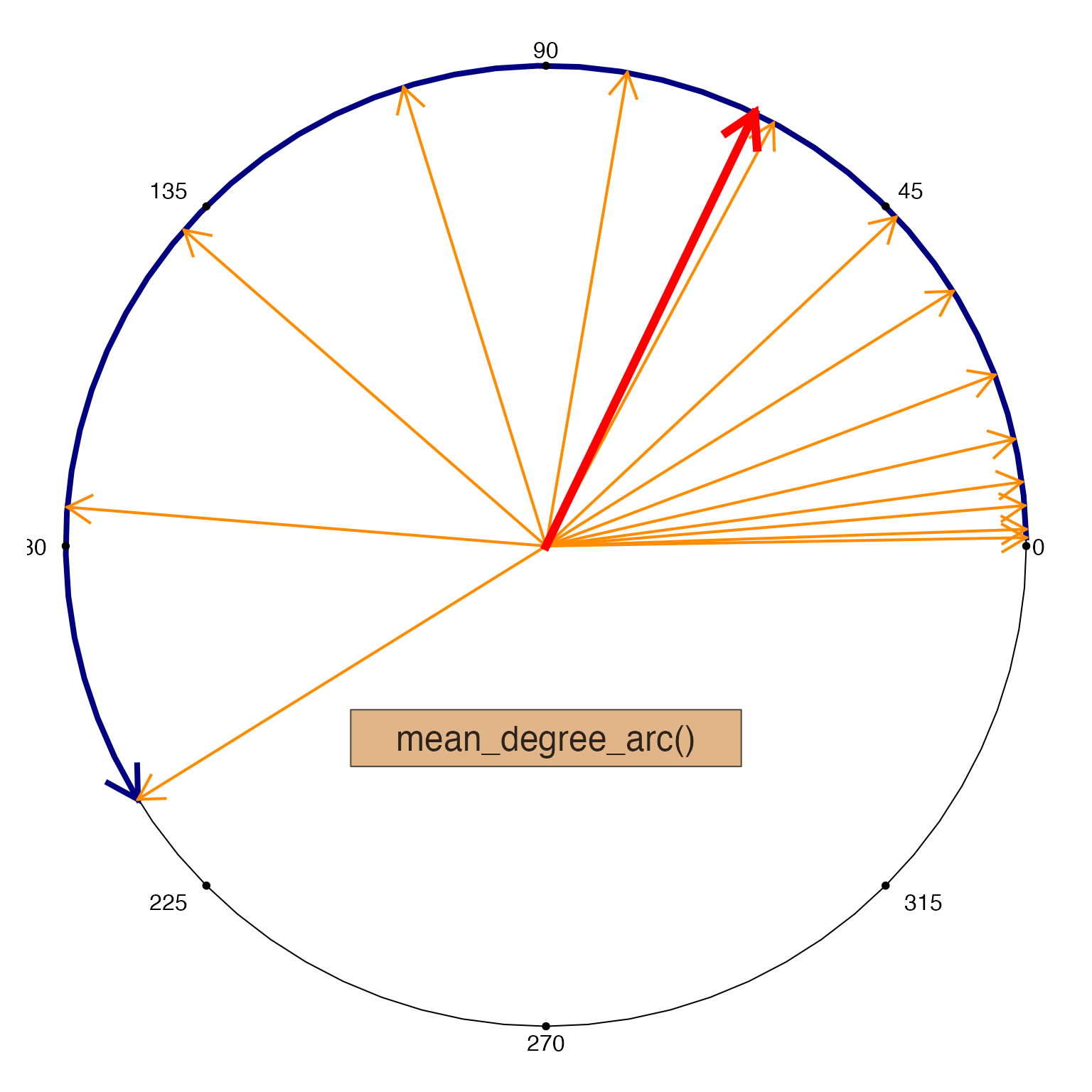 #> [1] 106.4214
#> attr(,"radius")
#> [1] 1
x <- x + 235;
mean_degree_arc(x, do_plot=TRUE);
#> [1] 106.4214
#> attr(,"radius")
#> [1] 1
x <- x + 235;
mean_degree_arc(x, do_plot=TRUE);
 #> [1] 299.2686
#> attr(,"radius")
#> [1] 1
mean_degree_arc(x, use_median=TRUE, do_plot=TRUE);
#> [1] 299.2686
#> attr(,"radius")
#> [1] 1
mean_degree_arc(x, use_median=TRUE, do_plot=TRUE);
 #> [1] 272.6235
#> attr(,"radius")
#> [1] 1
mean_degree_arc(x, use_range=TRUE, do_plot=TRUE);
#> [1] 272.6235
#> attr(,"radius")
#> [1] 1
mean_degree_arc(x, use_range=TRUE, do_plot=TRUE);
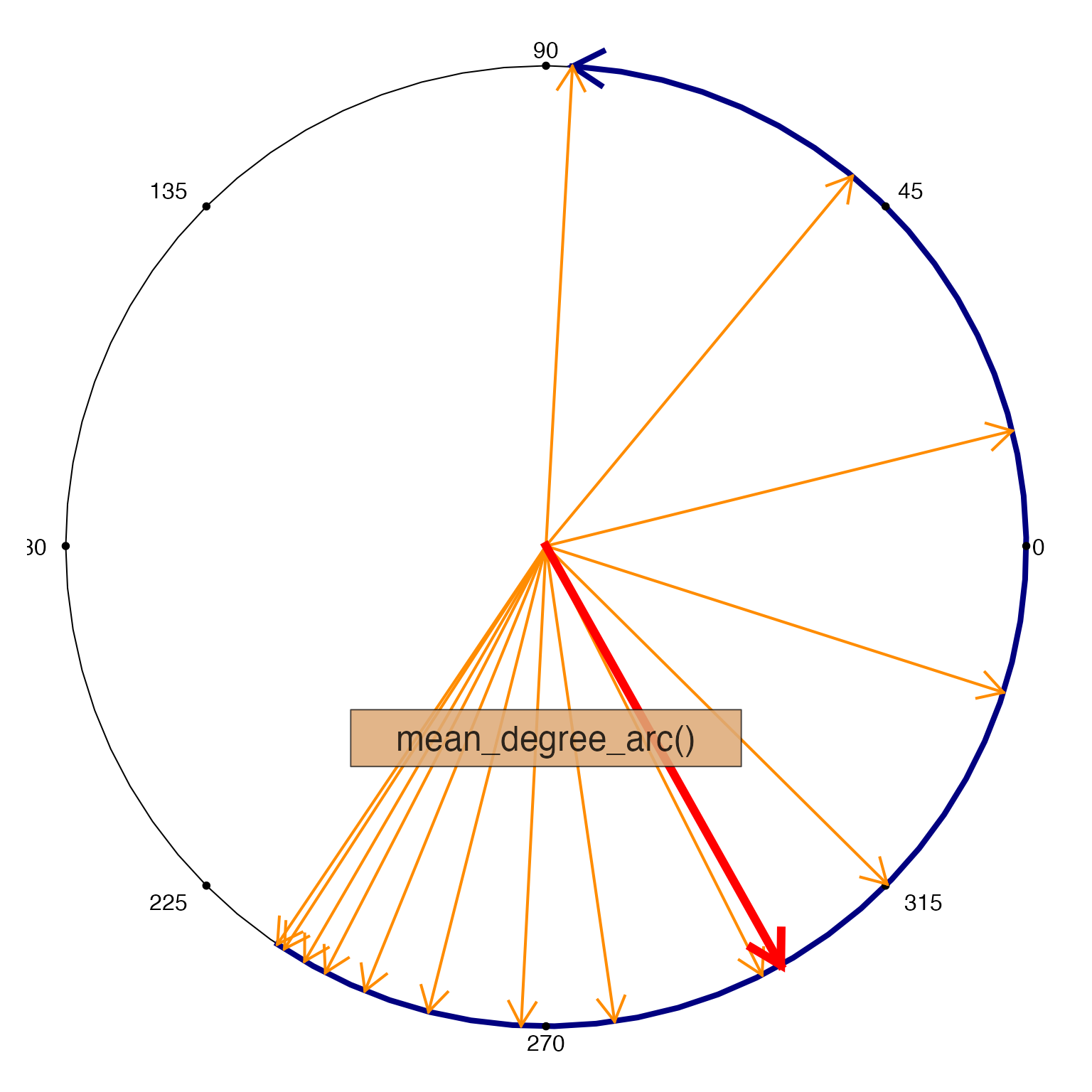 #> [1] 341.4214
#> attr(,"radius")
#> [1] 1
#> [1] 341.4214
#> attr(,"radius")
#> [1] 1